
| Legal Information |
|

The following describes how to configure a Small Business Server (SBS) 2000-based server that has a single network adapter to use a router to access the Internet. You can use the procedure that is described in this article to resolve the following issues:
There are a separate procedures for configuring a server that has two network adapters to connect to a router for Internet access and also for configuring a server that has a dial-up connection to access the Internet.
In the configuration that is described here the DNS server is the pivotal point for Active Directory and local area network (LAN) connectivity. Active Directory clients (including the server and its services) use DNS to locate domain controllers for administration and logon purposes. You must have a DNS server installed and configured for Active Directory for the associated client software to function correctly.
Because of the combination of server programs, the requirements for compatibility, and the many ways these programs can be configured, you must run SBS Internet Connection Wizard on the server.
Internet Connection Wizard supports connections to virtually any ISP, regardless of the connection type-broadband, router, Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), or analog modem. You can use Internet Connection Wizard to configure Windows 2000 networking for LAN and wide area network (WAN) connections, Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server for internal and Internet e-mail, and Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server.
It is also necessary to gather certain configuration information before using the ICW.
The information supplied here assumes that the SBS-based server has at least one network adapter that has a statically assigned Internet Protocol (IP) address. Do not configure the server as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client.
If you use a router for Internet access, the IP address on the router and the IP address on the server must be unique values on the same subnet. By default, the SBS network adapter is assigned an IP address of 192.168.16.2 and a subnet address of 255.255.255.0. This address is a private network address and on a class C subnet.
By default, most routers are not configured to work in this subnet. Some routers are preconfigured to use an IP address of 192.168.0.1 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (this address is also a private IP address in a class C subnet). You may have to change either the routers, the servers, or both IP address so that both addresses are on the same subnet.
The following configuration is an example of a working IP scheme for the SBS-based server and router:
IP address for SBS-based server: 192.168.16.2To give you greater flexibility to create a working IP address scheme when you follow the procedure that is described in this article, sections of the following address settings are replaced with variables:
Default gateway for SBS-based server: 192.168.16.1
Internal IP address for router: 192.168.16.1
Internal and SBS-based server subnet mask for the router: 255.255.255.0
SBS-based server IP address: 192.168.X.ZThe following table describes the variables that are used in these settings:
SBS-based server default gateway: 192.168.X.Y
Internal IP address of router: 192.168.X.Y
Internal IP address of router: 192.168.X.Y
Internal subnet mask of router : 255.255.255.0
| Variable | Value |
| X | Third octet in IP address that is used by all systems on LAN between 0 and 255 (the SBS default is 16). This value must be the same on the router, the SBS-based server, the client computer, and any other devices that require an IP address on the network. |
| Y | The router IP address, which is a unique value on the network, (a typical value is 1). |
| Z | The server IP address, which is a unique value on the network, (typical value is 2). |
| C | The client IP address, which is a unique value between 10 and 254 |
The following procedure describes how to configure the SBS-based server for internal and external connectivity. In this configuration, the server that is running ISA Server is not being used as a firewall; it is used only as a caching server. You can remove ISA Server from the server.
To configure the SBS-based server for internal and external connectivity:
Confirm that the SBS installation has the following settings:
IP Address
IP Address: 192.168.X.ZDNS Server address
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.X.Y
Preferred DNS server: 192.168.X.Z
Alternate DNS server: no settings
Before starting, you may wish to inspect the flow-chart associated with the ICW procedure.
The Small Business Server Internet Connection Wizard (ICW) can be started from the Small Business Server Console in a couple of ways.
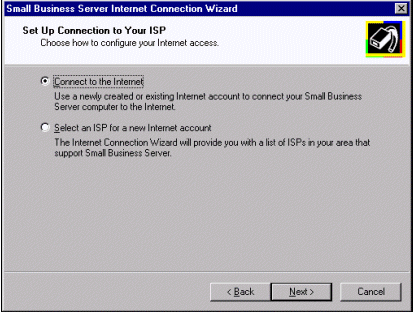
In some cases these ISPs provide an online sign-up that configures the appropriate Small Business Server services. By selecting Select an ISP for a new Internet account, you launch the Internet Connection Wizard. The ICW then dials the Microsoft Referral Server and downloads a list of ISPs that have special offerings for Small Business Server customers. Therefore, in order to take advantage of this feature, you must have a functional modem on your server.
If it supports online sign-up, once your new ISP has received your user, system, and billing information, the sign-up server generates an .ins file that is downloaded to your server. This .ins file will configure your dial-up networking connection, Proxy Server, Microsoft Exchange Server, and the information required by the Web Publishing Wizard. Some ISPs distribute sign-up floppy disks. If your ISP does this and is configured specifically for Small Business Server, you will not need to use the Small Business Server Internet Connection Wizard. Follow the instructions included with the sign-up disk to continue the installation.
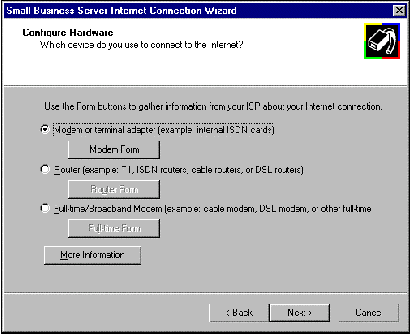
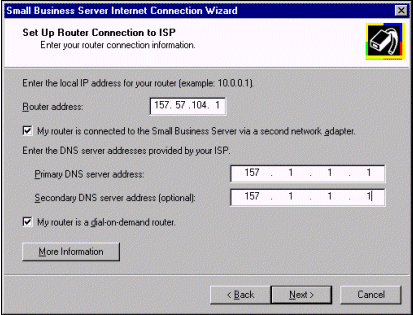
If your router is not a full-time connection (for example, if it is a demand-dial ISDN router), select the My router is a dial-on-demand router option. When this option is selected, the Exchange Internet Mail Service will be configured to forward outgoing mail to the SMTP relay host specified later in the Configure SMTP Mail Delivery page.
The Configure Internet Mail Settings page configures Small Business Server to use Internet e-mail. If you are using SMTP e-mail through Exchange Server, select the Use
Exchange Server for Internet mail option, which activates the Microsoft Exchange Internet Mail Service in Small Business Server. This is the option to choose, whether you host your own Internet domain and SMTP mail through a full-time connection or you dial in to an ISP that queues your mail until you connect.
Selecting Disable Exchange Server Internet Mail will disable the Microsoft Exchange Server Internet Mail Service. This option disables only Internet mail through Exchange Server; it does not affect the ability to send mail to others on the local Small Business Server-based network.
If you have already configured or customized your Exchange Server settings and do not wish to override these settings, select Do not change my Exchange Server settings.
If you will be retrieving e-mail from POP3 mailboxes at your ISP instead of directly through SMTP, select the Use POP3 for Internet mail option.
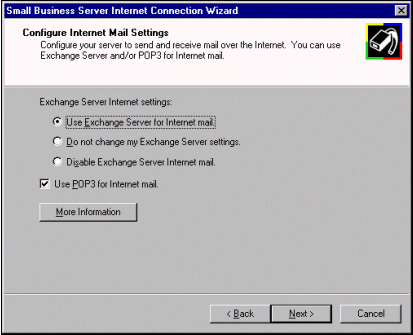
NOTE: You can also use the Internet Connection Wizard to configure POP3. For more information about how to configure POP3, click More Information in the Internet Connection Wizard.
NOTE: The example in the wizard assumes that mail is sent to "user@microsoft.com"; therefore "microsoft.com" is entered. Substitute "microsoft.com" for your Internet domain name.
If in the Configure Internet Mail Settings page you select the option Use Exchange Server for Internet mail, the wizard presents the Configure SMTP Mail Delivery page. This page will allow you to configure the sending properties of the Microsoft Exchange Internet Mail Service. The choices available to you depend on the connection typ, e: for a demand-dial router connection or a dial-up connection, select the Forward all mail to host option.
If you do not have a full-time connection to the Internet, you should select Forward all mail to host, which covers dial-up connections, dial-on-demand routers, or any connection that does not maintain a full-time Internet connection. This option will set the Internet Mail Service to forward all messages to an SMTP relay host provided by your ISP. This relay host can be entered by its IP address or fully qualified domain name (for example, exchange1.isp.com or 192.168.16.1). If a dial-up connection is established through this wizard, the option to use DNS is unavailable.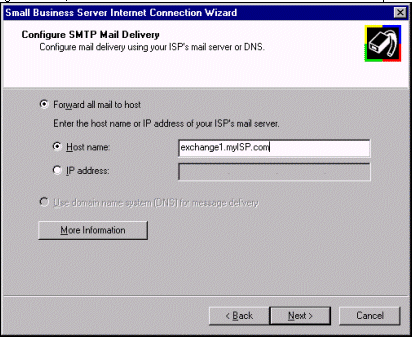
NOTE: The example in the wizard assumes that mail is sent to "user@microsoft.com"; therefore "microsoft.com" is entered. Substitute "microsoft.com" for your Internet domain name. A Domain Name needs to be configured as well.
NOTE: If your ISP blocks direct message delivery, e-mail messages are delivered to your ISP's mail server, which forwards these messages to their destination. If your ISP blocks direct message delivery, contact the ISP for more information.
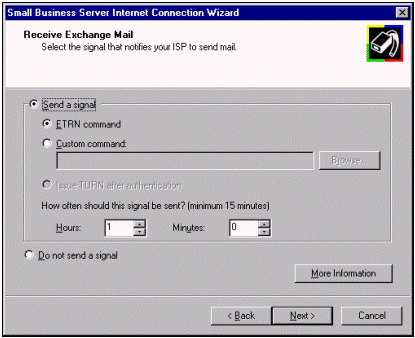
NOTE: You can turn on Message dequeuing if you require this functionality for mail retrieval. Before you do so, confirm this setting with your ISP.
For more details on receiving mail, click here.
Microsoft recommends that you use the DHCP service on either the router or the SBS-based server to the configure client. Do not configure the DHCP service on both devices; you must turn off the DHCP service on one of the devices. Microsoft recommends that you use the Windows 2000 DHCP server and that you turn off the router's DHCP server.
The following example describes a DHCP scope that works in a majority of configurations. This example assumes you are using the default setting provided with the SBS installation.
To view the DCHP scope:
| Option | Name | Vendor | Value |
| 003 | Router | Standard | 192.168.X.Y |
| 006 | DNS Servers | Standard | 192.168.X.Z |
| 044 | WINS/NBNS Servers | Standard | 192.168.X.Z |
| 046 | WINS/NBT Node Type | Standard | 0x1 |
| IP Address Field | IP Address Setting | Notes |
| IP address | 192.168.X.C | C is a unique value for each client computer |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Default Gateway | 192.168.X.Y | IP address of router |
| Preferred primary | DNS192.168.X.Z | IP address of server |
| Alternate secondary DNS | blank | |
| Primary WINS | 192.168.X.Z | IP address of server |
| Secondary WINS | 192.168.X.Z | IP address of server |
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |