
| Legal Information |
|

Two configurations, or network topologies, are commonly used to connect to the Internet through a router. The Small Business Server ICW supports both configurations.
In the first topology ("Router Configuration A"), the router is connected directly to the local area network (LAN). The router's internal Internet protocol (IP) address is set as the default gateway for each computer on the LAN, so the router handles clients' requests for resources outside the available local addresses (addresses beyond the LAN, on the Internet). This topology requires every client on the LAN to have a valid IP address unless the router is doing network address translation (NAT).
In the second topology ("Router Configuration B"), the router connects to the LAN through a second network adapter installed in the Small Business Server-based computer. The server's first network adapter connects the server to the LAN, and the second adapter connects the server to the router, which in turn connects to the Internet. The server's TCP/IP configuration has no default gateway on the internal network adapter, but the default gateway is configured on the external network adapter. No default gateway is configured on the clients because they will connect to the Internet through the Microsoft Proxy Server firewall.
The second topology is more secure because it takes advantage of the Proxy Server firewall features in Small Business Server. All incoming and outgoing packets must go through Small Business Server before being routed to their intended destination, so Proxy Server can monitor the packets and prevent outsiders from reaching your LAN.
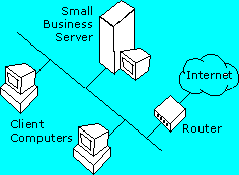 | 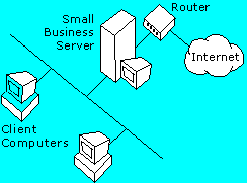 |
| Router Configuration A | Router Configuration B |
To correctly configure Small Business Server for Internet connectivity through a router, you will need the following information:
A broadband connection requires a second network adapter configured with a static IP address, which must be configured before using the wizard, and:
There are Word worksheets for each of the different Internet connection types
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |