Recovering Site Replication Service (SRS) involves restoring the SRS database. You can use Backup to restore the SRS database.
Note Alternatively, you can manually restore the SRS database (Srs.edb file) if you have a backup of that file. The Srs.edb file is located in the SRSData folder under the folder where you installed Exchange.
If you are restoring the SRS database as part of recovering a server running Exchange 2000, complete the necessary steps to restore or rebuild your server before you perform the following procedure. For example, if you are rebuilding an Exchange 2000 server running SRS, you must restore the local SRS database after running Exchange 2000 Setup in Disaster Recovery mode.
For information about when to restore SRS, see "Exchange 2000 Member Server Recovery Procedures" later in this chapter. For information about how to back up the SRS database, see "Backing Up Exchange 2000 Site Replication Service".
To restore the SRS database
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Microsoft Exchange, and then click System Manager.
- In Exchange System Manager, in the console tree, expand Tools, and then expand Site Replication Services to locate the server running SRS. Under Site Replication Services, there is at least one entry called Microsoft Exchange Site Replication Service , where is the name of the server running SRS
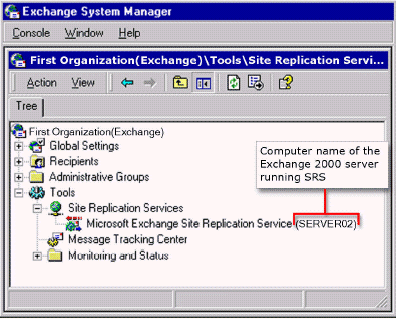
Exchange 2000 SRS
- On the server running SRS, click Start, click Run, type services.msc, and then click OK.
- In Services, in the details pane, double-click Microsoft Exchange Site Replication Service.
- In Microsoft Exchange Site Replication Service Properties, in the Startup Type box, select Automatic.
- Next to Service status, ensure that status is set to Stopped, and then click Apply. Do not close Microsoft Exchange Site Replication Service Properties.
- In Windows Explorer, move or delete any files that exist in the srsdata folder on the server running SRS. The original SRS database files cannot be restored if these files are present. To move or delete these files:
- On the server running SRS, click Start, point to Programs, point to Accessories, and then click Windows Explorer.
- In Windows Explorer, create a temporary folder to hold the files that you want to move or copy.
- On the Tools menu, click Folder Options.
- On the View tab, under Advanced Settings, ensure that the Hide file extensions for known file types check box is cleared, and then click OK.
- In Windows Explorer, in the console tree, go to the srsdata folder. By default, the location for this folder is C:\Program Files\Exchsrvr\srsdata, where C is the location where you installed Windows 2000 Server.
- Select all existing .edb, .log, or .chk files from the srsdata folder. From the Edit menu, click Move To Folder, and then specify a temporary folder. Alternatively, if you want to delete these files, right-click the files, and then click Delete. The advantage to archiving these files is that the set of files may be helpful if your SRS database restore job is unsuccessful.
- In Microsoft Exchange Site Replication Service Properties, under Service status, click Start.
- Click Start, point to Programs, point to Accessories, point to System Tools, and then click Backup.
- Click the Restore tab, and then, in the console tree, click the backup media you want to restore. If the correct media does not display under File, you may need to rebuild the catalog. For more information about how to rebuild the catalog, see "Rebuilding a Catalog for a Restore".
- Click the computer name\Microsoft Site Replication Service\SRS Storage check box, where is the name of your Exchange 2000 server that is running SRS .
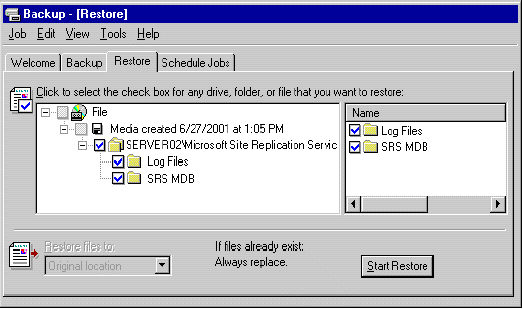
Restoring Exchange 2000 SRS
- In the Restore files to list, select the location to where you want the file restored. By default, the location specified is Original Location.
- Click Start Restore.
- In Restoring Database Store, in the Restore to box, specify to which server running Exchange 2000 you want the databases restored. This must be the server that is running SRS .
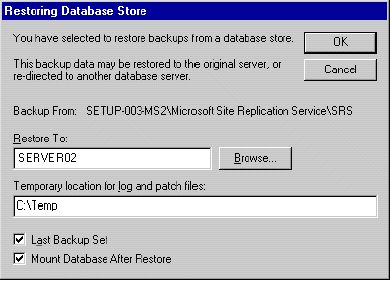
The Restoring Database Store dialog box
- In the Temporary location for log and patch files box, specify a directory to store log and patch files during the restore process.
Important If the directory that you specify in the Temporary location for log and patch files box is the same as the original location of the database or log files, the restore process will fail.
- If you are restoring a backup that is the only one in its set (for example, if you are restoring a Normal backup that does not have any Differential or Incremental backups), select the Last Backup Set check box. If you are restoring a backup that is part of a series of Normal, Differential, or Incremental backups, leave this check box cleared until you restore the final Incremental or Differential backup in the series. The restore process does not play back the SRS log files and patch files to the database being restored until this box is selected.
Note The Mount Database After Restore check box does not affect your SRS database restore. That control is applicable only to mailbox and public folder store restoration procedures.
- If Backup prompts you for the location of the backup file to use in the restore, select the correct backup name, and then click OK. For more information about how to select the correct backup file name, see "Sat control is applicable only to mailbox and public folder store restoration procedures.
- After the restore process is complete, the Restore Progress dialog box displays. Ensure that the restore process was successful. For more information about how to check the success of the restore process, see "Checking the Success of a Completed Restore Job".
- After you verify that the SRS database backups are successfully restored, in the Restore Progress dialog box, click Close. You are then prompted to restart your computer to complete the restore. Click Yes to restart.
- Perform any further steps required by your disaster recovery process, such as installing Exchange service packs.
- On the Administrative Group object to which the server belongs, retype the Exchange 5.5 service account password. If you do not retype this password, the SRS service will not start, and you will have trouble communicating directly with Exchange 5.x servers. To retype the Exchange 5.5 service account password, in Exchange System Manager, on the Administrative Group object to which the server belongs, open the Properties dialog box, and then retype the Exchange 5.5 service account password (you do not have to change the password).
The information in this article applies to:
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 Enterprise Edition
- Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 Standard Edition
- Microsoft Windows Small Business Server 2003, Premium Edition
- Microsoft Windows Small Business Server 2003, Standard Edition
- Microsoft Exchange 2000 Server




