
| Legal Information |
|

ISA is a Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server. This is a fully-fledged firewall. ISA 2000 takes full advantage of Microsoft Windows 2000. It's a Web-caching server and it takes full advantage of Windows 2000 Active Directory. Windows 2000 Active Directory helps us to integrate ISA 2000 with all its advanced technologies. An ISA Server can use Microsoft Active Directory to provide centralised, scaleable management capabilities.
ISA 2000 basically protects your internal computer from the Internet by installing packet filters. This is similar to Proxy 2.0. ISA Server, which also protects all communications between internal computers and the Internet.
You need a computer with a 300 MHz (or faster) Pentium II-compatible processor. You need to run Windows 2000 Server with Service Pack 1 or later, Windows 2000 Advanced Server with Service Pack 1 or later, or Windows 2000 Datacenter Server.
You need to have 256 MB of RAM, 20 MB of available hard disk space, and a Windows 2000-compatible network adapter for communicating with an internal network card.
It is advisable to have two network cards on an ISA machine. One for the internal network and one for the Internet connection. You need one hard disk partition formatted with the NTFS file system for Web caching.
ISA Server will have two network cards. If you have one network card, then it's a Web-caching server only. Internet is connected to one network card and your internal network. It's a very basic configuration.
ISA Management. Internet access can be done with access policy. Here we configure all of the policies. It is a manageable and scaleable snap-in. With one snap-in, you see all of the areas on the single enterprise. Administrators benefit from a single management interface for firewall and Web caching.
ISA is built for enterprise. It provides tiered policy management. That means on the enterprise level, you can set up a policy and that policy will be pushed down to area levels. Then you can further manage those policies on the area level per user, per group, per computer. ISA allows local area policies.
It can inherit policies from enterprise levels. In a distributed environment, administrators can delegate various levels of ISA administration. That means you can delegate administration jobs to each area and level of ISA computer.
ISA Server can also monitor requests and responses between the Internet and internal client computers, controlling who can access which computers on the corporate network. You can use the client set address of which computers you are allowing to access the Internet and which you are prohibiting to access the Internet. You can set the client address sets of different computer sets that you are allowing to access the Internet. You can set any sort of protocol rules. IP packets filtering is based on those client address sets.
ISA Server can be deployed as a dedicated firewall that acts as a secure gateway on the Internet for internal clients. Proxy 2.0 was a debatable product that is not a fully-fledged firewall.
ISA Server is a fully-fledged firewall with an outgoing access policy, intrusion detection, smart application filters, authentication, and a Security Wizard. It also does do statefull inspection. It's a circuit-level or session-level firewall, unlike Proxy 2.0. It doesn't do IP to IP mapping or one-to-one IP.
You can lock down your ISA Server based on the Windows 2000 security template.
There are smart application filters on ISA 2000. These application filters can be seen under Network Configuration. It controls the application-specific traffic with data-aware filters
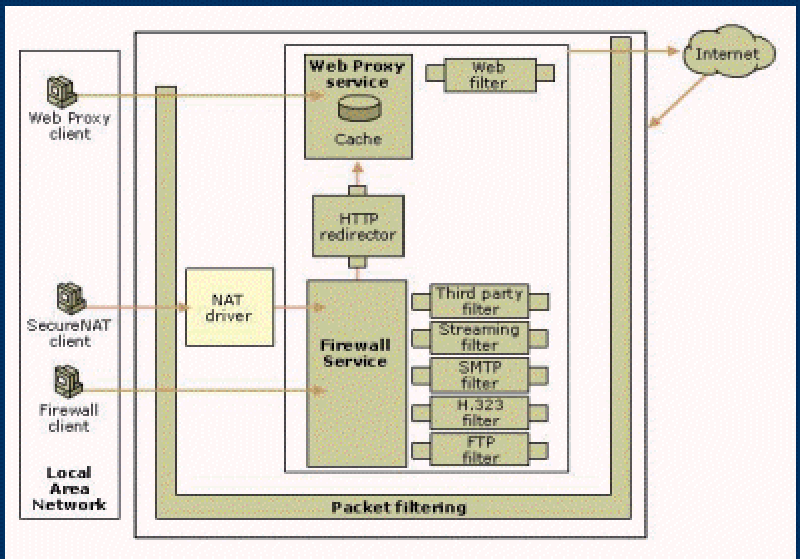
The following is an overview of the ISA 2000 architecture. It's very basic. There are three ways ISA's internal client can access the Web set:
Let's say you have two network cards on the ISA box. One is your public IP address and one is your private IP address. On the client side, all you have to do is point your gateway to the internal IP entrance of the ISA box. That way you've configured SecureNAT and ISA will NAT the address and pass it to the Internet.
So there are three ways.
This is a picture of the Web Proxy service, caching, HTTP redirector, and firewall service.
Third-party filters can be used, a streaming filter, an SMTP filter, an H.323 filter, and an FTP filter. Those are the filters available under application filters under Network Configuration.
There is also a feature called "Extensibility." Extensible administration, application filters, Web filters, extensible user interface, extensible alerts, and extensible storage. On ISA, different reports can be logged that are viewable as HTML pages.
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |