
| Legal Information |
|

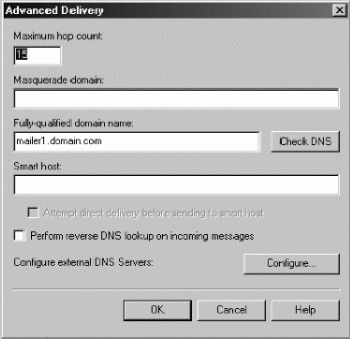
When you want to put extra controls on how DNS is used with a particular virtual server, you have several options. You can enable reverse DNS lookups, or you can specify an explicit list of external DNS servers to use for name resolution.
With reverse lookups enabled, Exchange Server attempts to verify that the mail client's IP address matches the host and domain submitted by the client in the start session command. If the IP and DNS information match, Exchange Server passes the message through without modifying its contents.
If Exchange Server can't verify the IP and DNS information, Exchange Server modifies the message header so that the key word "unverified" is inserted on the Received line of the message header.
Reverse lookups can severely affect Exchange Server's performance, and this performance impact increases as the number of concurrent users and connections increases. Because of this, you'll want to be very cautious about enabling reverse lookups.
DNS servers are used to resolve host and domain names for message delivery. Internal DNS servers are used to resolve host and domain names within the organisation, and external DNS servers are used to resolve names outside the organisation. Normally, the list of DNS servers that you want to use for name resolution is configured in the TCP/IP settings for the Exchange server.
If necessary, you can override these settings for external servers. You do this by defining an external DNS server list for an individual virtual server.
Once the external DNS server list is created, the SMTP virtual server uses only the servers on that list. If you want to keep using some or all of the local DNS servers, you must manually add those IP addresses to the list.
To enable reverse DNS lookups or define an external DNS server list, complete the following steps:
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |