
| Legal Information |
|

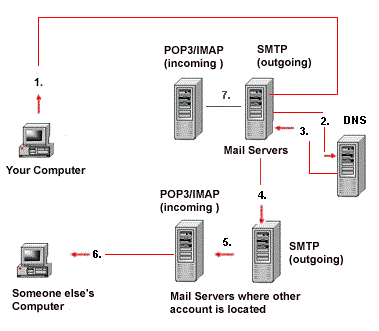 | The Mail User Agent (MUA) is used to create an e-mail message. It is sent to a server, the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA). The MTA is responsible for transferring the message to a single server or collection of additional MTA servers, where it is finally delivered. The client software (i.e., the MUA) communicates directly with a Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server, the MTA uses SMTP, which does nothing more than deliver messages from one server to another. Using DNS lookup, a sending MTA (MTA 1) then communicates with another MTA. In the DNS zone, for the receiver address' domain, there will be an MX record. This is a DNS resource record that specifies the mail server of a domain. So, after the DNS lookup, a response is given to the requested mail server with the IP address of the recipient's mail server. In this way the 'to' mail server is identified. The system sends a request to find out the corresponding MTA of the recipient. This will be done with the help of the Mail Exchanger (MX) record. | .
If the protocol used is IMAP, then the email message is stored in the mail server itself, but the user can easily manipulate the emails on the mail server as in the local computer.
This is the difference when using both the protocols and this is how your email gets delivered. If some error occurred to send the email, the emails will be delayed. There is a mail queue in every mail server. These mails will be pending in the mail queue. The mail server will keep trying to resend the email. Once the email sending fails permanently, the mail server may send a bounce back email message to the sender's email address<
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |