
| Legal Information |
|

The actual sequence of commands to construct and send a message using the SMTP protocol consists of a "HELO" message to open the communications channel followed by the commands "MAIL," "RCPT," and "DATA" each with the appropriate data to form the email header and message. Extended HELO (EHLO) is the Extended Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (ESMTP) command equivalent of HELO
Finally, the connection is terminated using the "QUIT" command.
The figure belowt shows a breakdown of the sequence of commands in sending an email
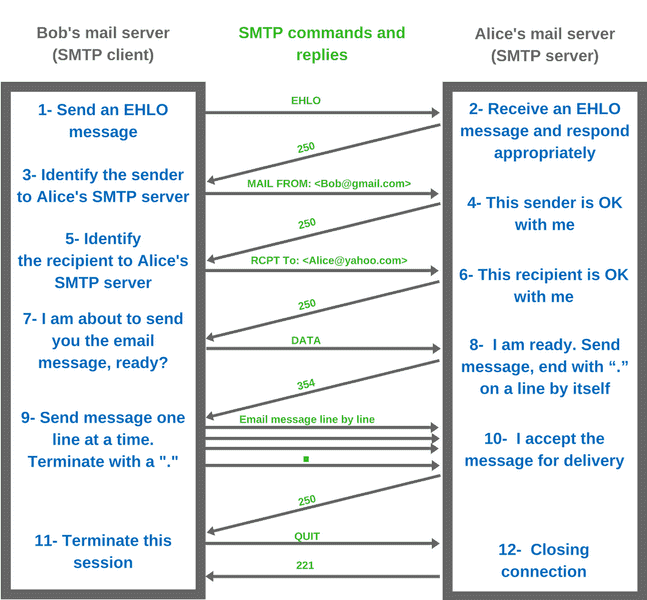 |
The SMTP handshake .The general purpose of the handshaking stage is for the client and the server to identify themselves, the services they can provide, and to identify the identities of the sender and the recipient of the email.
It starts with the sending mail server sending an EHLO command to the receiving mail server and identifying its domain. For example, the sending mail server would send "EHLO The SMTP server it the receiving domain (e,g. yahoo.com) acknowledges the EHLO message by responding with code "250" along with the services that the SMTP server can support. It's important for the client and server to agree on the services and features they can support before the message transfer starts. The SMTP client resumes by sending a "MAIL FROM" command along with the sender information. In our scenario, it would be something like "MAIL FROM: The handshaking stage is now complete. |
The message transfer
Before starting the actual message transfer, the SMTP client sends one more command called "DATA" to the server just to make sure that the server side is ready.
The receiving mail server responds with code "354" indicating that it's ready to receive the message. After receiving this code from the server, the client is now ready to send the email message.
The actual email message is sent out line by line. The server side though does not acknowledge each individual line received. It just waits for the "End of Mail" special line which is a line that only has a "." (period or full stop) by itself.
When the client sends a "." to the server, this indicates that the client is done with sending the email message. This also tells the server that it can start processing the message now.
After the receiving mail server receives the ".", it acknowledges receiving the whole message by sending a 250 code back to the client.
Closing the connection
This is very simple and straightforward. The sending mail server sends a "QUIT" command to the receiving mail server to indicate its intention to close the connection to whicthw receiving mail server responds with a "221" code.
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |