
| Legal Information |
|

Active Directory stores information about network elements in the form of objects. These objects can be assigned attributes, which describe specific characteristics about the object. This lets companies store a wide range of information in the directory and tightly control access to it.
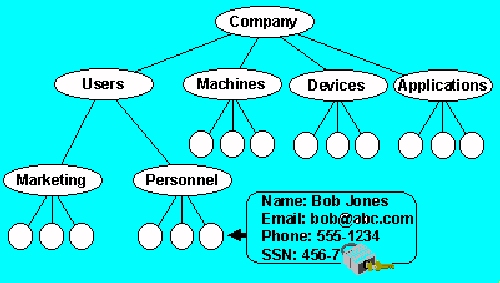
As illustrated in Figure 2 above, object- and attribute-level security lets administrators precisely control access to information stored in the directory.
For example, a user object stored in the directory for Bob Jones has attributes for Bob's name, e-mail address, phone number, and Social Security number. The Active Directory lets administrators assign access privileges for each attribute of the object, as well as for the entire object.
In this case, the system administrator has allowed global access to the Bob Jones object, but has locked access of the Social Security Number attribute.
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |