Good Knowledge Is Good2Use

Most SMTP processing occurs in IIS rather than in the Internet Mail Service.
- The SMTP engine component receives SMTP requests on TCP port 25 and creates an ImailMsg object for incoming messages.
- The ImailMsg object is passed to the advanced queuing component, which places the message in the PreCatQueue and relays the message to the message categorises component. The message is returned after its destination has been determined.
- The ImailMsg object is placed in the PreRoutingQueue when the route for the message is determined. The Advanced Queuing Component then queues the message for delivery, taking into account next-hop routing information supplied by the routing engine.
- The Advanced Queuing Component delivers the message either to the local Web Storage System or causes the SMTP service to send the message outbound using SMTP. The message is delivered to Web Storage System in the event that it is destined for a local recipient, public folder, or the Message Transfer Agent for transfer to other Exchange 5.5 or earlier servers through RPC, or X.400. The protocol portion of the SMTP service processes regular outbound messages for other Exchange 2000 servers through the SMTP protocol.
The following shows a representation of the Exchange 2000 SMTP process.
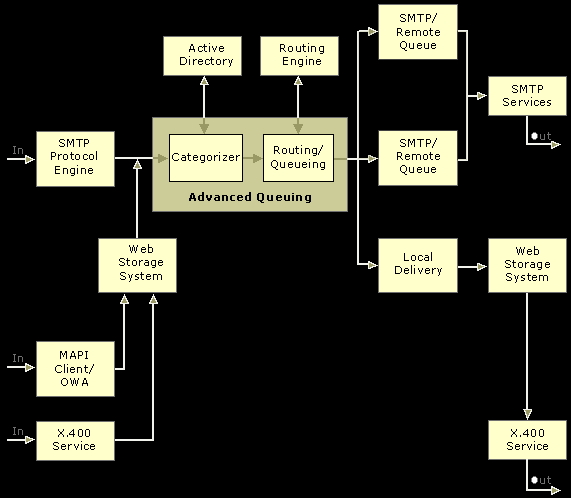
SMTP process
Windows 2000 Server includes a native SMTP component designed to be a basic implementation of the protocol. Windows 2000 and other products can use this transport to perform operations such as directory replication. Because SMTP is part of IIS 5.0, it installs with Windows 2000 and it is extended in Exchange 2000. It runs as part of the Inetinfo.exe process. It supports basic distribution list expansion features. It cannot act as a ListServer, and it cannot route messages based on topology link status.
© Copyright 1998-1999 GOOD2USE


