
| Legal Information |
|

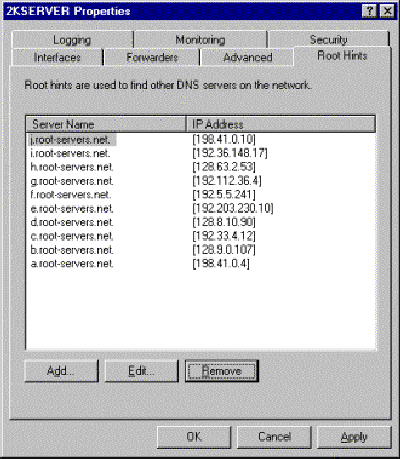
Windows 2000 DNSs come configured with root hints and no forwarders. Root hints are used to find the servers at the root of the Internet hierarchical system.
Using root hints is not really effective for most corporations. It is just too slow to start looking through the entire hierarchy unless you're an ISP.
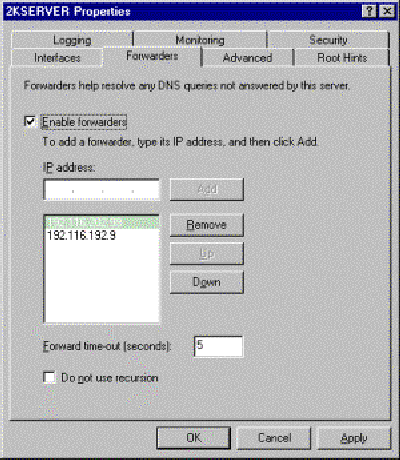
Instead, forwarders can be configured forward request from clients to DNS servers on the Internet, typically your ISP DNSs. ISP DNSs are usually fast and employ large cached information on Internet domains.
The benefits of using this configuration are that the Exchange 2000 machine can also connect to the Internet also for updates and online error reporting. The local DNS also does some caching by itself so some queries don't even go the ISP DNSs and resolve locally.
To configure forwarders and delete root hints, using the Administrative Tools DNS MMC, go to the property sheet of your DNS server.
The information in this article applies to:
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |