
| Legal Information |
|

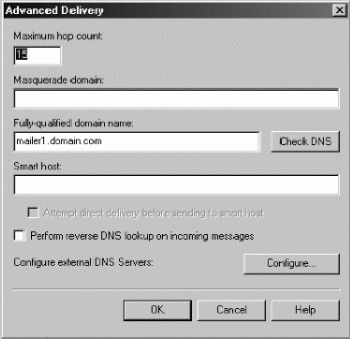
Domain names play an important role in determining how mail is delivered in the enterprise, and you have two options for configuring domain name usage. You can set a masquerade domain, or you can set a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for the SMTP virtual server.
A masquerade domain replaces the local domain name in any Mail From lines in the message header. Mail From information is used to determine the address for sending nondelivery reports and doesn't replace the From lines in the message body that are displayed to mail clients. The name replacement occurs on the first hop only.
The fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the Exchange server is used in mail delivery. The server must have a FQDN, and this FQDN is associated with an e-mail domain through a DNS mail exchanger record. In Exchange
Server you have two options for specifying an FQDN:
The name in the Network Identification tab is used automatically. If you change the name in this tab, the new name is used the next time the computer is rebooted. No action is required to update the FQDN for the virtual server.
However, if you want to override the setting in the network identification tab, you can do so by specifying a unique FQDN for the SMTP virtual server.
You can set the masquerade domain name or override the default FQDN by completing the following steps:
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |