
| Legal Information |
|

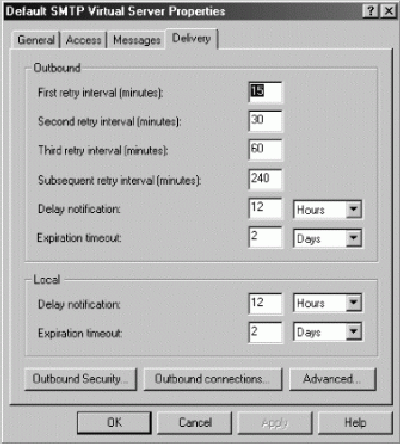
Once a connection has been established and the receiving computer has acknowledged that it's ready to receive the data transfer, Exchange Server attempts to deliver messages queued for delivery to the computer. If a message can't be delivered on the first attempt, Exchange Server tries to send the message again after a specified time. Exchange Server keeps trying to send the message at the intervals you've specified until the expiration time-out is reached. When the time limit is reached, the message is returned to the sender with a nondelivery report. The default expiration time-out is two days.
After each failed attempt to deliver a message, Exchange Server generates a delay notification and queues it for delivery to the user who sent the message. Notification doesn't occur immediately after failure. Instead, Exchange Server sends the delay notification message only after the notification delay interval and then only if the message hasn't already been delivered. The default delay notification is 12 hours.
The way in which Exchange Server handles delay notification and expiration time-out values depends on whether the message originated within or outside the organisation. Exchange Server handles messages that originate within the organisation using the Local delay notification and expiration time-out values. Exchange Server handles messages that originate outside the organisation using the Outbound delay notification and expiration time-out values.
Tip A copy of the failed message and the nondelivery report can be sent to your organisation's postmaster or other administrator's inbox. To do this, follow the procedure outlined in "Managing Message Delivery for SMTP and the Exchange Server Organisation."
You can view or change the retry interval, delay notification, and expiration time-out by completing the following steps:
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |