
| Legal Information |
|

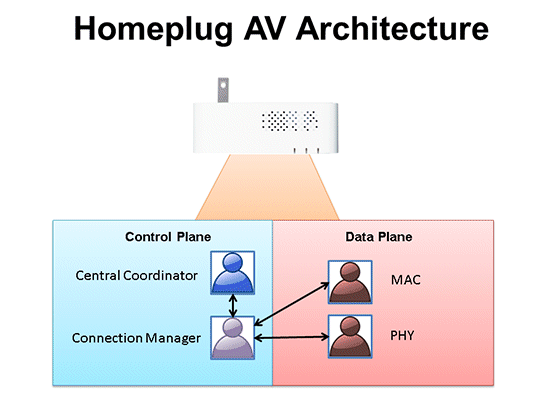 | The Connection Manager has two sub-functions - MAC and PHY. Performance at the PHY is achieved via windowed Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) and Turbo Convolutional Code (TCC). IEEE 1901 is the standard that covers power line networking and allows for OFDM or Wavelet modulation for the PHY. |
As to the many devices, ODFM splits the available bandwidth into a lot of different channels, multiple channels can be used for different things at 1 time. Device A and B are talking on channel 1 while device A and C are talking on channel 2, etc. OFDM is a channel-management mechanism that can split the available spectrum into sub-spectrum sizes for data transmission. The key benefit in OFDM is multi-path transmission. It's not necessary to wait for a particular lane to clear because there are multiple lanes from over which data can be sent. OFDM is also the basis for 4G LTE, WiMAX, and other multiple access systems. . | 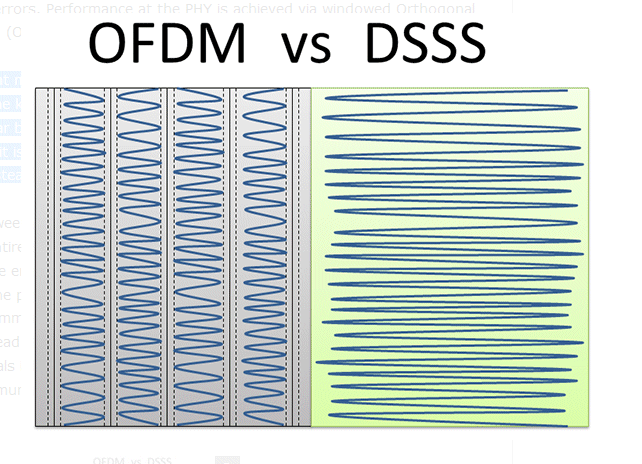 |
Following the PHY is the Media Access Control (MAC) layer, referenced in the OSI Model as Layer 2. It's at this layer Quality of Service (QoS) features are handled via Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) and Collision Sense Multiple Access/Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA).
This layer is also where the Central Coordinator asserts order throughout the Powerline network through the use of three control regions: Beacon, CSMA and Contention-Free.
First, the Central Coordinator sets a Beacon Period in which it broadcasts a schedule to all Powerline adapters, instructing each node its permitted time frame to send traffic, whether that traffic is Contention-Free or CSMA.
When establishing the Beacon Period, the Central Coordinator syncs it to the AC Line Cycle, which is when the AC current "wave" is pulsed down the wire. Each node then specifies through the Contention-Free region its QoS requirements to meet traffic demand.
If the Central Coordinator can handle the request, it instructs the Powerline adapters to choose the transmission frequency.
This "Tone Map", along with an estimation of channel usage, is sent to the Central Coordinator so it can determine the lifespan of the connections. When persistent bandwidth isn't required, perhaps for interactive types of traffic (think telnet or ssh), allocated time in the Beacon Period may be used by a Powerline adapter to send traffic using CSMA.
Because the QoS mechanisms are reliant on timing, once the Central Coordinator broadcasts the Beacon packet, the MAC synchronizes his swatch upon inspection of the associated timestamp.
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |