
| Legal Information |
|

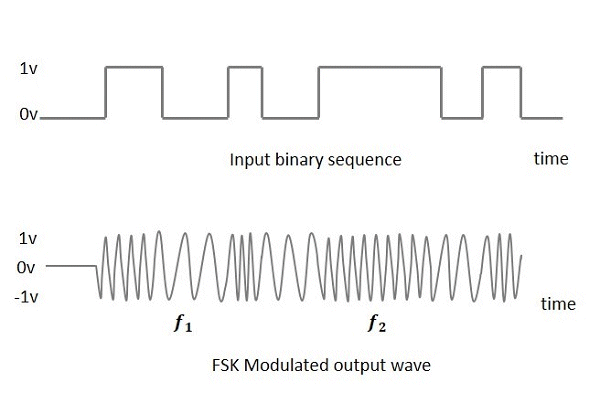 | Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) is the digital modulation technique in which the frequency of the carrier signal varies according to the digital signal changes. FSK is a scheme of frequency modulation.The output of a FSK modulated wave is high in frequency for a binary High input (1) and is low in frequency for a binary Low input (0). The binary 1s and 0s are called Mark and Space frequencies. The image left is the diagrammatic representation of FSK modulated waveform along with its input. This contrasts with Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) which represents the binary data in the form of variations in the amplitude of a signal.. Any modulated signal has a high frequency carrier. The binary signal when ASK modulated, gives a zero value for Low input while it gives the carrier output for High input. |
| FSK operates in one of two modes, a modulator that modulates a signal to be transmitted and a demodulator to demodulate the signal at the receiving end
The FSK modulator comprises of two oscillators with a clock and the input binary sequence shown in the block diagram. right. The two oscillators produce a higher and a lower frequency signals and are connected to a switch along with an internal clock. | 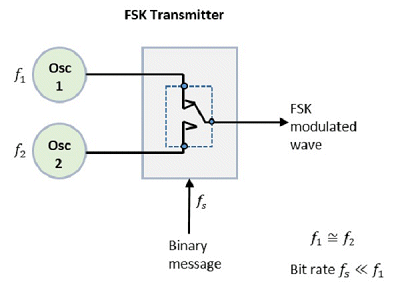 |
||
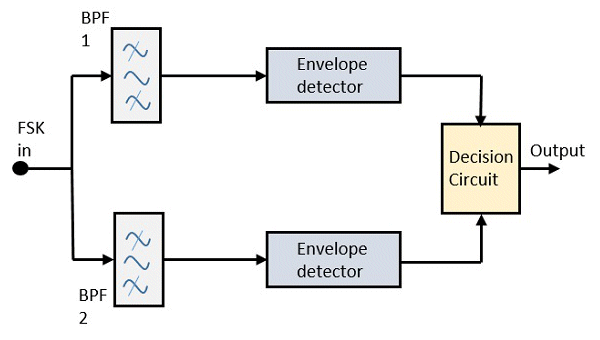 | There are different methods for demodulating a FSK wave. The two main methods are asynchronous and synchronous demodulation. Synchronous transmissions have mark-to-space and space-to-mark transitions in synchronism with a reference clock. Asynchronous signals do not require a reference clock but instead rely on special bit patterns to control timing during decoding The synchronous method is a coherent one and asynchronous detector is a non-coherent one.
The block diagram left is of an asynchronous FSK detector consisting of two band pass filters, two envelope detectors, and a decision circuit. |
||
| The block diagram of Synchronous FSK detector (right) consists of two mixers with local oscillator circuits, two band pass filters and a decision circuit. The FSK signal input is given to the two mixers with local oscillator circuits. These two are connected to two band pass filters. These combinations act as demodulators and the decision circuit chooses which output is more likely and selects it from any one of the detectors. The two signals have a minimum frequency separation. | 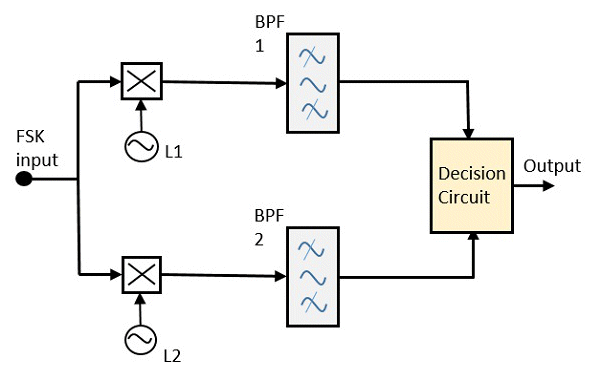 |
For both of the demodulators, the bandwidth of each of them depends on their bit rate. This synchronous demodulator is a bit complex than asynchronous type demodulators.
| Search Knowledge Base | Feedback |